

The below figures depict the way that the cathode ray is effected by magnetics.

It was George Stoney who first gave the term electrons to the cathode rays. Thompson (1856-1940) concluded that cathode rays are negatively charged particles that are located in all atoms. Another significant property of cathode rays is that they are deflected by magnetic and electric fields in a manner that is identical to negatively charged material. These phosphors showed that cathode rays travel in straight lines and have properties independent of the cathode material (whether it is gold, silver, etc.). Cathode rays produced by the CRT are invisible and can only be detected by light emitted by the materials that they strike, called phosphors, painted at the end of the CRT to reveal the path of the cathode rays. The radiation crosses the evacuated tube to the positive terminal, the anode. Cathode rays are a type of radiation emitted by the negative terminal, the cathode, and were discovered by passing electricity through nearly-evacuated glass tubes. The first cathode-ray tube (CRT) was invented by Michael Faraday (1791-1867). The atomic theory led to the creation of the law of multiple proportions. Dalton’s atomic theory also explains the law of constant composition: if all the atoms of an element are alike in mass and if atoms unite in fixed numerical ratios, the percent composition of a compound must have a unique value without regards to the sample analyzed. It correctly explains the law of conservation of mass: if atoms of an element are indestructible, then the same atom must be present after a chemical reaction as before and, and the mass must constant. However, these failures do not justify discarding the atomic theory. The second rule was proven incorrect by the discovery that not all atoms of the same element have the same mass there are different isotopes. The first rule was proven incorrect when scientists divided atoms in a process called nuclear fission. The gold and copper atoms combine in a simple numerical ratio.ĭalton's theory has not proven to be correct under all circumstances. Pure gold mixed with pure copper forms rose gold. A pure gold necklace and a pure silver necklace are different because they have different atoms. A pure gold necklace is made up of atoms. Figure 6: Created by Jessica ThorntonĪtomic theory can be used to answers the questions presented above.
The second equation for the reaction is incorrect because half of an atom does not exist. The illustration below describes this rule.

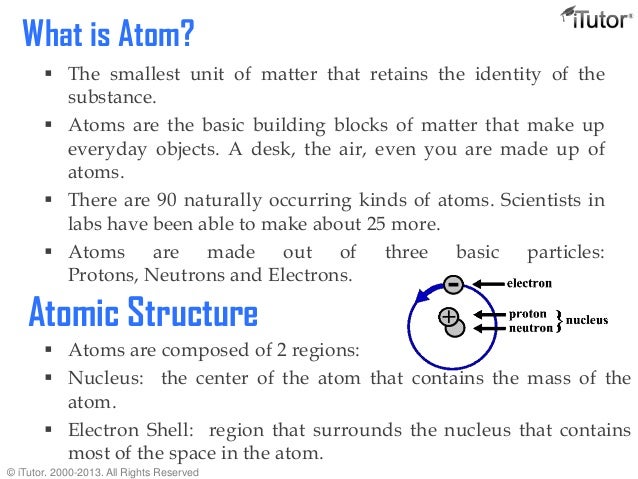
For each compound, different elements combine in a simple numerical ratio. Figure 5 (silver): Courtesy of /./photogallery/ģ. For example, gold and silver have different atomic masses and different properties.įigure 4 (Gold): Courtesy of Chris Ralph that released this image into the public domain. All atoms of an element are alike in mass and other properties, but the atoms of one element differ from all other elements. Figure 3: Courtesy of Yzmo on Wikimedia commons, available under Creative Commons-Share Alike 3.0 UnportedĢ. The following sections discuss this further. The black area around the nucleus represent the electron cloud. The purple and red dots represent the neutrons and protons in the nucleus. Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed. Each chemical element is composed of extremely small particles that are indivisible and cannot be seen by the naked eye, called atoms. Figure one as a whole constructed by Jessica Thornton using Microsoft Word and Preview (UCD). Scientists did not take into account the gases that play a critical role in this reaction. However, the illustration below shows that the burning of word does follow the law of conservation of mass. From this observation scientists concluded that mass had been lost. If this law was true, then how could a large piece of wood be reduced to a small pile of ashes? The wood clearly has a greater mass than the ashes. Historically, this was a difficult concept for scientists to grasp. The law of conservation of mass was formulated by Antoine Lavoisier (1743-1794) as a result of his combustion experiment, in which he observed that the mass of his original substance-a glass vessel, tin, and air-was equal to the mass of the produced substance-the glass vessel, “tin calx”, and the remaining air. The law of conservation of mass states that the total mass present before a chemical reaction is the same as the total mass present after the chemical reaction in other words, mass is conserved.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
